what is Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, Care, Medication, Diet, Family and Friends’ Cooperation, Treatment, and Support, 9 points

hi friends, do you want to know what is Arthritis? so an article for you.
Arthritis is a multifaceted and pervasive health condition, impacting millions of individuals across the globe. This comprehensive guide will provide you with an in-depth understanding of arthritis, delving into its complex causes, diverse symptoms, meticulous care requirements, medication options, dietary considerations, the indispensable role of family and friends cooperation, and a comprehensive exploration of the various treatment modalities available. We aim to offer you a resource that is not only informative and easily digestible but also optimized for search engine visibility (SEO) to ensure that you have access to the most current information on this subject.
point 1. What is Arthritis?
Arthritis, an umbrella term encompassing over 100 distinct joint diseases, is characterized by inflammation, pain, and stiffness within affected joints. While osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most prevalent forms, there exist numerous other variations, each with its unique characteristics.
point2: Arthritis Causes
Understanding the intricate factors contributing to arthritis’s development is essential for both effective management and preventative strategies. The following factors play pivotal roles in the genesis of arthritis:
a. Genetic Predisposition:
Some forms of arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis, exhibit a pronounced genetic predilection, often running within families and generationally inherited.

b. Age-Related Degeneration:
Osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis, frequently arises due to the natural aging process, characterized by wear and tear on the joints over time.
c. Autoimmune Reactions:
In rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the synovium, the membranous lining surrounding the joints.
d. Infectious Agents:
Certain forms of arthritis, such as reactive arthritis, can be triggered by infections within the joints.
e. Environmental Influences:
Factors such as smoking, exposure to specific toxins, and infections may increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing arthritis.
f. Physical Trauma:
Joint injuries, fractures, or dislocations can induce post-traumatic arthritis, a type of arthritis that develops subsequent to physical injuries.
point 3: Arthritis Symptoms
Recognizing the diverse array of symptoms associated with arthritis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Common arthritis symptoms encompass:
a. Joint Pain:
A prevailing hallmark of arthritis, patients experience persistent pain within one or more joints, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating agony.
b. Joint Stiffness:
Arthritis often manifests as morning stiffness within the affected joints, hampering daily activities and mobility.
may you like to read:https://drreactivate.com/healthy-eating-for-teens/
c.Swelling and Inflammation:
Inflamed joints may appear red, and swollen, and feel warm to the touch, accentuating discomfort.
d.Limited Range of Motion:
Arthritis frequently restricts joint mobility, resulting in diminished flexibility and functionality.
e.Fatigue:
Many arthritis patients grapple with extreme fatigue, often feeling drained and devoid of energy.
f. Structural Deformities:
In advanced stages, specific types of arthritis can lead to permanent joint deformities, further impeding movement and causing aesthetic alterations.
g.Systemic Involvement:
Rheumatoid arthritis, in particular, can affect various body systems, causing systemic symptoms such as fever, unexplained weight loss, and the formation of nodules under the skin.
point 4: Arthritis Care
Properly managing arthritis necessitates specific care practices that significantly enhance the individual’s quality of life. Here are the fundamental aspects of arthritis care:
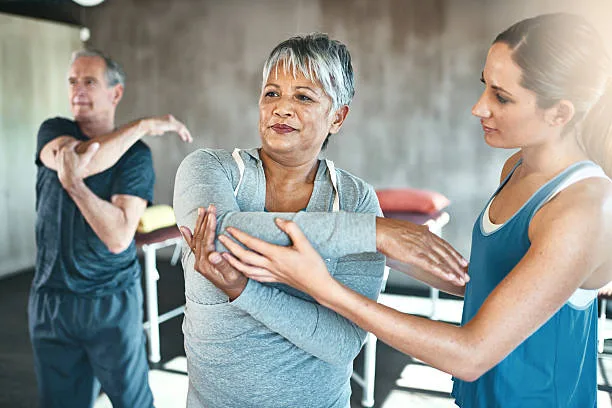

may you like to read:https://drreactivate.com/understanding-schizophrenia/
a. Physical Activity and Exercise:
Regular engagement in low-impact exercises such as swimming and walking helps maintain joint mobility and muscle strength, promoting overall physical well-being.
b. Rest and Recovery:
Striking a balance between activity and rest is essential, as overexertion can exacerbate arthritis symptoms, necessitating adequate time for joint recuperation.
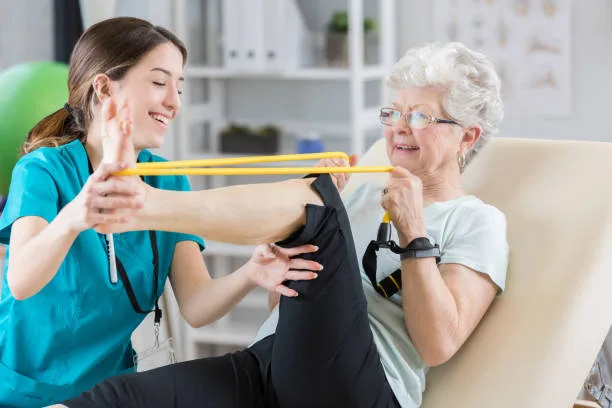

c. Joint Protection Techniques:
Utilizing assistive devices, and ergonomic tools, and adopting correct body mechanics are critical measures to safeguard joints from unnecessary strain and injury.
d. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount in reducing the burden on joints, particularly for individuals with osteoarthritis.
e. Medications:
Varied medications, including pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), play essential roles in arthritis symptom management.
f.Physical Therapy:
Collaborating with a skilled physical therapist results in the development of tailored exercise routines and strategies that enhance joint function, reduce pain, and bolster physical resilience.
point 5: Arthritis Medication
Medication constitutes a critical component in the arsenal against arthritis. The following medications are commonly employed in arthritis management:
a. Pain Relievers:
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen, as well as prescription opioids, are instrumental in alleviating pain and enhancing overall comfort.
b.Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
NSAIDs serve as potent agents in curbing inflammation and alleviating pain, making them pivotal in arthritis symptom management.
c.Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
These pharmaceuticals assume a central role in restraining the progression of autoimmune forms of arthritis, primarily rheumatoid arthritis.
d.Biologics:
Biologic medications are designed to specifically target components of the immune system responsible for initiating inflammation, offering a potent therapeutic option for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune conditions.
e.Corticosteroids:
These medications, while effective in swiftly mitigating inflammation, may entail side effects upon prolonged use, making them a short-term solution for symptom management.
f.Pain Management Techniques:
Alternative strategies like acupuncture, heat and cold therapy, and localized joint injections can provide considerable relief, enhancing the individual’s comfort and quality of life.

point 6: Arthritis Diet
Diet exerts a considerable influence on arthritis symptoms and overall health. Below are dietary considerations for individuals with arthritis:
a. Anti-Inflammatory Foods:
The consumption of foods rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids is instrumental in reducing inflammation and enhancing overall well-being.
b.Weight Control:
Adhering to a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight has the dual benefit of alleviating strain on joints, particularly in cases of osteoarthritis.
c. Avoidance of Trigger Foods:
Some individuals may identify specific foods, such as nightshades or red meat, as exacerbating their arthritis symptoms. Maintaining awareness and making necessary dietary adjustments can mitigate discomfort.
d.Hydration:
Adequate hydration is essential for preserving joint health and supporting various bodily functions, necessitating vigilance in maintaining proper fluid intake.
e.Supplements:
Some dietary supplements, including glucosamine and chondroitin, have shown potential in providing relief for individuals with osteoarthritis.
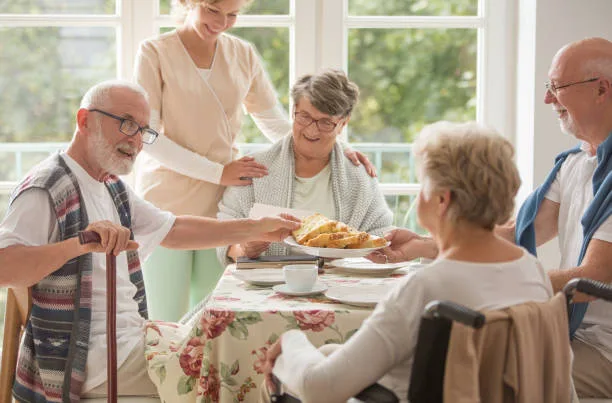

point 7: Family and Friends’ Cooperation
The support and cooperation of family and friends are indispensable for individuals living with arthritis. Here’s how loved ones can effectively collaborate:
a. Emotional Support:
Compassion, understanding, and empathy are pivotal in helping individuals with arthritis cope with the physical and emotional challenges that often accompany the condition.
b. Assistance with Activities of Daily Living:
Simple acts of assistance in daily tasks and providing transportation can considerably alleviate the burdens faced by arthritis patients.
c. Open Communication:
Encouraging open and honest communication is instrumental in addressing concerns, setting goals, and planning for the future in a way that is both realistic and empowering.
d. Self-Education:
Family and friends should undertake an active role in educating themselves about arthritis, fostering a deeper understanding of the condition, its challenges, and available resources.
point 8: Arthritis Treatment
Treatment for arthritis is multifaceted, with the approach contingent upon the type and severity of the condition. The following treatment modalities are commonly employed:
a. Medications:
As previously detailed, medication regimens can provide symptomatic relief and, in the case of DMARDs, slow the progression of specific types of arthritis.
b.Physical Therapy:
Collaborating with a physical therapist enables individuals to access a tailored exercise regimen that improves joint function and reduces pain, ultimately enhancing overall physical capability.
c. Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapists work in tandem with arthritis patients to adapt their daily routines, enabling them to cope with and manage their symptoms more effectively.
d. Surgical Intervention:
In severe cases of arthritis, surgical procedures, such as joint replacement or synovectomy, may be necessary to restore joint function and alleviate pain.
e. Alternative Therapies:
Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and the utilization of herbal remedies, may be integrated into treatment plans to enhance overall well-being and augment the effectiveness of traditional treatments.
point 9: Support Groups and Organizations
Dealing with arthritis can be isolating, but numerous support groups and organizations are dedicated to providing valuable resources and fostering a sense of community for individuals grappling with this condition. Prominent entities in this realm include:
a. Arthritis Foundation:
As a leading organization, the Arthritis Foundation offers an array of services, including education, advocacy, and support, to facilitate the empowerment and enhancement of the lives of arthritis patients.
b.Online Forums and Communities:
In the digital age, an abundance of online platforms, forums, and communities cater to individuals seeking to share their experiences, gain insights, and seek advice from others who share similar challenges.
c. Local Support Groups:
Many cities and regions host in-person support groups, creating opportunities for individuals to establish connections, share experiences, and draw strength from others facing similar adversities.
Conclusion
Arthritis, a complex and often debilitating condition, affects millions of people globally. Gaining an in-depth comprehension of its multifaceted causes, recognizing its diverse symptoms, and adhering to proper care measures are essential for managing the condition. When combined with appropriate medication, dietary strategies, and various treatment modalities, individuals living with arthritis can lead fulfilling lives. Staying informed, actively engaging with support groups and organizations, and fostering cooperation with healthcare professionals are essential components in the journey toward enhanced health and well-being for those impacted by arthritis.
FAQs
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation and stiffness of the joints, which can result in pain, swelling, and decreased joint mobility.
How many types of arthritis are there?
There are over 100 different types of arthritis, with the two most common being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
What causes arthritis?
The causes of arthritis can vary depending on the type. Osteoarthritis is often associated with wear and tear on the joints, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition. Other types of arthritis may have different underlying causes.
What are the common symptoms of arthritis?
Common symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, reduced range of motion, and warmth or redness in the affected joints.
Who is at risk for developing arthritis?
Arthritis can affect people of all ages, but the risk increases with age. It can also be influenced by genetics, lifestyle factors, and underlying medical conditions.
Can arthritis be prevented?
While some risk factors for arthritis, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and avoiding joint injuries can help.
How is arthritis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and various imaging and lab tests. A rheumatologist is a specialist who often diagnoses and treats arthritis.
What are the available treatment options for arthritis?
Treatment for arthritis may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery. The specific treatment plan depends on the type and severity of the arthritis.
Are there any natural remedies or alternative treatments for arthritis?
Some people find relief from arthritis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, dietary supplements, or herbal remedies. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any alternative treatments.
Can arthritis be cured?
Most types of arthritis are chronic conditions, and there is no cure. However, with appropriate management and treatment, many people can effectively control their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
What lifestyle changes can help manage arthritis?
Lifestyle changes like regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting enough rest can all contribute to better arthritis management.
Can children develop arthritis?
Yes, children can develop arthritis. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is the most common type of arthritis in children. It requires specialized care from pediatric rheumatologists.
What is the role of diet in managing arthritis?
Some people with arthritis find that certain foods or dietary patterns can either help or worsen their symptoms. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized dietary plan.
Is it safe to exercise with arthritis?
Exercise can be beneficial for arthritis, but it’s essential to choose activities that are joint-friendly and work with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop an appropriate exercise plan.
Can arthritis affect other parts of the body besides the joints?
Yes, arthritis can affect various body systems. Inflammatory arthritis types like rheumatoid arthritis can impact the heart, lungs, and other organs.

